Superposition of Waves
Superposition of Waves: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Superposition of Waves, Principle of Superposition of Waves, Interference of Waves, Equation of Resultant Wave after Interference, Condition for Constructive Interference, etc.
Important Questions on Superposition of Waves
Two light beams of intensities in the ratio of are allowed to interfere. The ratio of the intensity of maxima and minima will be :
Equation of resultant wave on string after interference :-
(iii) Two waves and are interfering one another. What will be the resultant amplitude.
Equation of resultant wave on string after interference :-
(ii) The amplitude of two interfering waves are respectively if the resultant amplitude is . The interference becomes.Equation of resultant wave on string after interference :-
(i) The amplitude of two interfering waves are respectively. The resultant amplitude in case if consructive interference.
Three harmonic waves having equal frequency and same intensity , have phase angles and respectively. When they are superimposed the intensity of the resultant wave is close to:
A travelling wave represented by is superimposed on another wave represented by . The resultant is a
When two progressive waves and are superimposed, the amplitude of the resultant wave is . Find the value of .
Two identical sources of sound and produce intensity at a point equi distant from source. If power of is reduced to and phase difference between two sources is varied then let is maximum intensity at point . Find
Two speakers connected to the same source of fixed frequency are placed apart in a box. A sensitive microphone placed at a distance of from their midpoint along the perpendicular bisector shows a maximum response. The box is slowly rotated until the speakers are in line with the microphone. The distance between the midpoint of the speakers and the microphone remains the same. Exactly five maximum responses are observed in the microphone in doing this. The wavelength of sound wave is (in ):
A wave represented by the equation is superposed with another wave to form a stationary wave such that the point is a node. The equation of the other wave is,
An organ pipe open at both ends produces:
The disturbances produced by two sound sources cannot be cancelled as the disturbance by each wave is added.
What do you understand by principle of superposition of waves?
The maximum intensity of fringes in Young's experiment is . If one of the slit is closed then, the intensity at that place becomes . Which of the following relations is true?
Three waves of equal frequencies having amplitudes and arrive at a given point with successive phase difference of The amplitude of the resulting wave in is given by,
Two waves are passing through a region in the same direction at the same time. If the equation of these wave are
,
then the amplitude of the resultant wave for is,
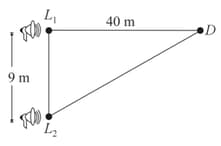
Two loudspeakers and driven by a common oscillator and amplifier, are arranged as shown. The frequency of the oscillator is gradually increased from Zero and the detector at D records a series of maxima and minima.If the speed of sound is then the frequency at which the first maximum is observed is:
The amplitude of a wave represented by displacement equation will be
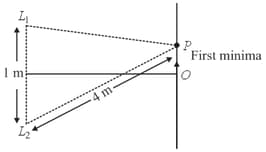
Two loudspeakers apart are coherent sources which emit sound waves of wavelength . A microphone moving along OP records the first minimum at . If is is equal to :
Principle of superposition for displacement is valid for :-
